We all know about Diabetes Mellitus to some extent as Diabetes Mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder that prevents the body from utilising glucose completely or partially. It is characterised by raised glucose concentration in the blood and alterations in carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism. But have you ever heard of Gestational Diabetes or Pregnancy Diabetes?
We all know about Diabetes Mellitus to some extent as Diabetes Mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder that prevents the body from utilising glucose completely or partially. It is characterised by raised glucose concentration in the blood and alterations in carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism. But have you ever heard of Gestational Diabetes or Pregnancy Diabetes?
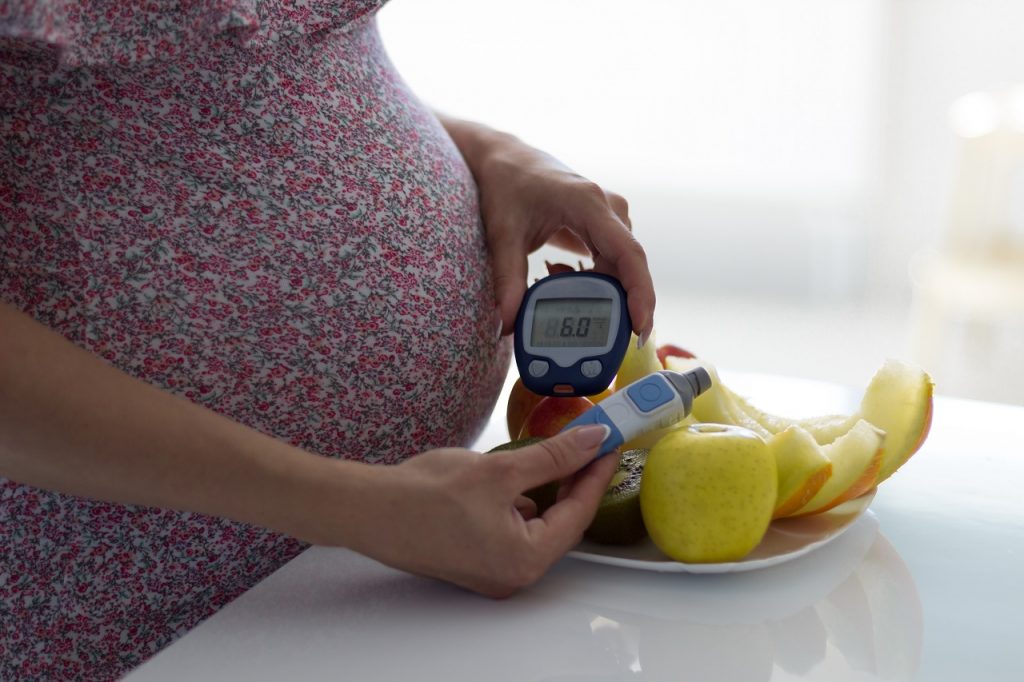
Gestational Diabetes is a high blood sugar (glucose) condition that develops during pregnancy and usually disappears after giving birth. It can happen at any stage of pregnancy, but is more common in the second or third trimester. Insulin requirements goes up one to three times in pregnancy. During normal pregnancy the level of plasma insulin is raised by the action of placental hormones thus placing a burden on the insulin secreting cells of the pancreatic islets. The pancreas may be unable to meet these demands in women genetically predisposed to develop both types of diabetes. Long term studies show that some 80% of women with gestational diabetes ultimately develop permanent clinical diabetes requiring treatment.
What Causes Gestational Diabetes?
The causes of Gestational Diabetes is not known clearly yet. Some, but not all women with gestational diabetes are found to be overweight before getting pregnant or have a family history of diabetes. It is more common in Native American, Alaskan Native, Asian and Black women, but white women may develop it due to poor lifestyle.
Are There Tests to Determine it?
Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) is a confirmatory test. The OGTT measures blood glucose after you fast for at least 8 hours. Firstly, the blood sample is drawn in fasting state. Then, 75g of glucose dissolved in 250-300 ml of water is given, Lemon juice may be added for flavour and to prevent nausea. Then the blood specimens are collected every 30 mins for 2-3 hours after the administration of glucose.
High blood glucose levels at any two or more blood test times – Fasting, 1 hour, 2 hours or 3 hours – mean you have Gestational diabetes.
Complications During Pregnancy
If blood sugar is not controlled, it can lead to problems for both maternal and foetal health. Uncontrolled diabetes during the first trimester of pregnancy increases the risk of abortions and congenital malfunctions in the foetus. Some of the major consequences are:
- High Blood Pressure (Preeclampsia): Preeclampsia is a potentially dangerous pregnancy complication characterised by high blood pressure. Due to the high blood pressure levels of the mother, the protein in urine spikes up and swelling in fingers and toes and lower body persists. High blood pressure can be harmful to both – the mother and the unborn baby. It might lead to the baby being born early and also could cause seizures or a stroke (a blood clot or a bleed in the brain that can lead to brain damage) in the woman during labour or delivery.
- An Extra Large Baby: Uncontrolled Diabetes in the mother causes the baby’s blood sugar to be high. The baby tends to “overfeed” and grows extra-large. Besides, causing discomfort to the mother, it can lead to problems during delivery causing prolonged labour pain which might need a C-section to deliver the baby. The baby can be born with nerve damage due to pressure on the shoulder during delivery.
- Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycaemia): People with diabetes who take insulin or other medications can develop blood sugar that is too low or hypoglycaemia. Low blood sugar can be very serious and even fatal if not treated quickly.
How to Manage Gestational Diabetes
The main modes of treatment of Gestational Diabetes include:
1. Eating a Healthy Diet: Dietary measures are an essential part of the treatment of diabetic patients whether they are on diet alone or on metformin drug or insulin. Carbohydrate restriction impairs insulin sensitivity and reversed by high carbohydrate diet but it needs to be maintained between 60-65% of total calories. So include more complex carbohydrates or polysaccharides like Multi-grain flour, Oats, Muesli, Granola, Amaranth, Pearl Millet (Bajra), Finger Millet (Ragi), Quinoa, etc. Studies have shown that raising carbohydrates does not adversely affect the fasting blood glucose levels, glucose tolerance or insulin requirements provided that total calories are not increased.
Along with carbs, include more protein-rich foods like pulses and lentils, Kidney beans (Rajma), Soya Bean, peas, beans, peanuts, milk and dairy products like yogurt, buttermilk, cottage cheese (paneer), eggs, chicken, etc. to ensure weight gain and prevent osteomalacia during pregnancy. Inclusion of fibre like fruits and green leafy vegetables are must as it improves glucose metabolism without increasing insulin secretion. It increases the intestinal transit-time, delay gastric emptying slow glucose absorption.
2. Drugs or Insulin Treatment: Metformin or Insulin therapy is the accepted medical management of gestational diabetes. Insulin is the first drug of choice and metformin can be considered after 20 weeks of gestation. Insulin must be taken without delay if it is suggested by the doctor.
3. Exercise: Stay Active to help keep your blood sugar under control. Exercise regularly – before, during and after pregnancy. Moderate exercise such as brisk walking for 30mins a day for 5 times a week is a good goal to set.
4. Monitoring Blood Sugar Often: Be aware that your blood sugar can change very quickly, becoming too high or too low depending on what you eat and how much you exercise and your growing baby’s blood sugar also varies several times during the day. Check your blood sugar level as often as directed by the doctor and any time you have symptoms.
By adopting these measures one can enjoy a healthy Antenatal period. For more articles on managing Diabetes, check out Healthy Reads or for further information or guidance, reach out to our certified experts by subscribing to GOQii’s Personalised Health Coaching here.
#BeTheForce
Disclaimer: The information provided in this blog is for general awareness and educational purposes only. It is not intended to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider for personalised medical guidance or concerns related to your health. Images shown are for representation purposes only and may not depict the exact recommendations or outcomes.
 By now, anyone conscious about their health is aware of
By now, anyone conscious about their health is aware of  You’ve been taking your blood pressure tablets for years. You rarely miss a dose. Yet, every time you check, those numbers stubbornly stay high.
You’ve been taking your blood pressure tablets for years. You rarely miss a dose. Yet, every time you check, those numbers stubbornly stay high.