Have you ever thought of why some foods can be eaten in good quantities without worrying about the sugar rise or weight increase while in some others portion control is important? Glycemic index is the concept that helps us to choose food wisely. Are you wondering what is glycemic index and how does it help?
Glycemic index or GI is a measure of the effects of carbohydrates on blood glucose levels. Carbohydrates that break down during digestion releasing glucose rapidly into the blood stream have a high GI; carbohydrates that break down slowly, releasing glucose gradually into the bloodstream, have a low GI.
A lower glycemic index suggests slower rates of digestion and absorption of the foods’. Carbohydrates may also indicate greater extraction from the liver and periphery of the products of carbohydrate digestion. A lower glycemic response is often thought to equate to a lower insulin demand, better long-term blood glucose control and a reduction in blood lipids.
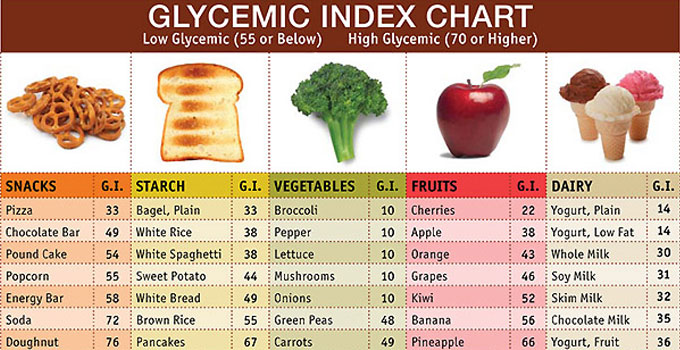
Glycemic index of foods
Glycemic index values can be interpreted intuitively as percentages on an absolute scale and are commonly interpreted as follows:
| Classification | GI range | Examples |
| Low GI | 55 or less | most fruit(apple, orange, peach, citrus fruits) and vegetables (except potatoes, watermelon), whole grainy breads, pasta, legumes/pulses, milk, curd products extremely low in carbohydrates (fish, eggs, meat, nuts, oils), brown rice, corn tortilla, wheat tortilla |
| Medium GI | 56 – 69 | whole wheat products, basmati rice, sweet potato, table sugar, most white rices ,Muesli, banana, Honey |
| High GI | 70 and above | Corn flakes, baked potato, watermelon, croissant, white bread, extruded cereals (e.g., Rice crispies), straight glucose (100), peanuts |
A low GI food will release glucose more slowly and steadily. A high GI food causes a more rapid rise in blood glucose levels and is suitable for energy recovery after endurance exercise or for a person with diabetes experiencing hypoglycemia.
Benefits of the Glycemic Index
Eating a lot of high GI foods can be harmful to your health as it pushes your body to extremes. This is especially true if you are overweight and sedentary. Switching to eating mainly low GI carbohydrates that slowly trickle glucose into your blood stream keeps your energy levels balanced and will feel fuller for longer between meals.
- Low GI diets help people lose and control weight
- Low GI diets increase the body’s sensitivity to insulin
- Low GI carbohydrates improve diabetes control
- Low GI carbohydrates reduce the risk of heart disease
- Low GI carbohydrates reduce blood cholesterol levels
- Low GI carbohydrates reduce hunger and keep you fuller for longer
- Low GI carbohydrates prolong physical endurance
- High GI carbohydrates help re-fuel carbohydrate stores after exercise
 Dates originate from date palm. This delicious fruit is always mistaken by people that it’s a weight gainer. Most are of the opinion that ‘Dates’ because of it sweetness can cause weight gain which is totally wrong. That is just a myth. ‘Dates’ in reality have many hidden benefits which I will take you through. The health benefits of dates are innumerable, it is in fact a dry fruit which is sweet in taste yet healthy and fat free.
Dates originate from date palm. This delicious fruit is always mistaken by people that it’s a weight gainer. Most are of the opinion that ‘Dates’ because of it sweetness can cause weight gain which is totally wrong. That is just a myth. ‘Dates’ in reality have many hidden benefits which I will take you through. The health benefits of dates are innumerable, it is in fact a dry fruit which is sweet in taste yet healthy and fat free.




