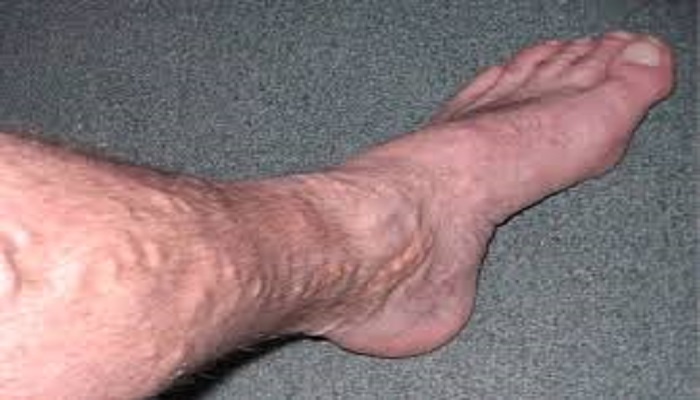
Varicose veins are a relatively common condition, often inherited, and women are at least twice as likely as men to develop them.
Varicose veins are enlarged, twisted, gnarled superficial veins that appear just under the skin’s surface. These can form in any part of the body but most commonly affect the legs.
Let’s explore what causes varicose veins and how to manage this condition.
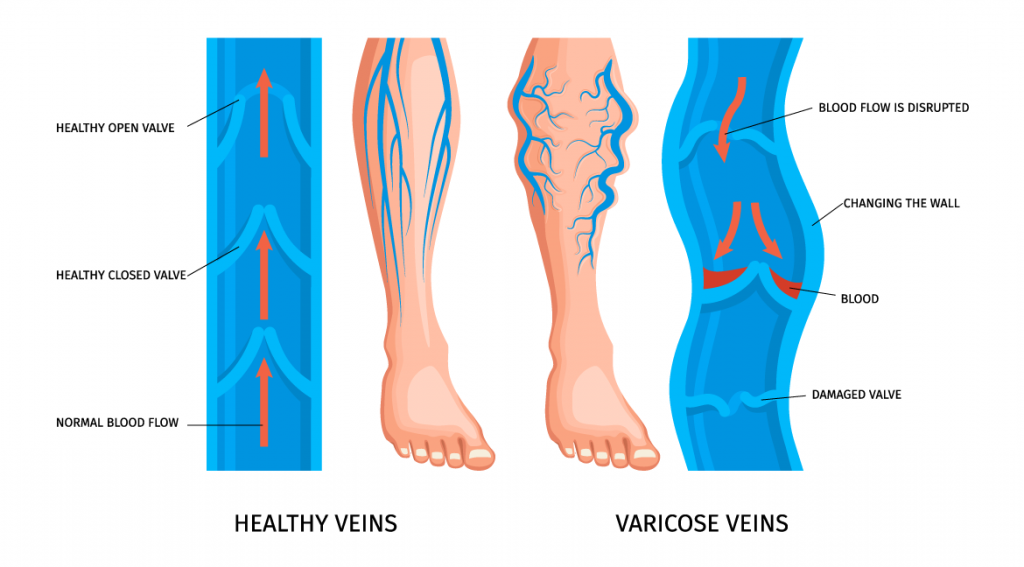
- Veins are blood vessels responsible for carrying blood from body tissues back to the heart, a challenging task since the blood here is moving upwards against gravity. To facilitate this, veins have small one-way valves that keep blood flowing towards the heart. When these valves become weak or damaged, blood can back up and pool in the veins, causing them to swell, widen, and bulge.
- A variant of varicose veins is known as spider veins, which are smaller red, purple, and blue vessels that also twist and turn. Spider veins are easily visible through the skin, typically on the legs and face.
- Varicose veins are primarily genetic which means the condition runs in families and certain factors like hormonal changes can increase the risk (as occurs in pregnancy).
- Did you always think that varicose veins affected women only? The truth is women are more commonly affected because female hormones tend to relax the walls and valves of the veins, however men get them too!
- Aging definitely worsens the problem of varicose veins, but young people can get it too!
- Are varicose veins only a cosmetic issue? On the contrary, they can be much more than that! A significant number of people with varicose veins eventually develop symptoms, most common being dull achiness, heaviness, throbbing, cramping and swelling of legs. Severe dryness and itchiness of skin near varicose veins is also common. Bleeding, skin discoloration, skin thickening and ulcers are other less common symptoms, but once skin damage occurs it is usually permanent.
- What to do if you have varicose veins? A visit to your doctor should be the first step. The doctor will examine any visible veins and may also do an ultrasound, which is a non-invasive test that utilizes high frequency waves and allows the doctor to see how blood is flowing in the veins.
Angiogram is another test where a dye is injected into veins and X-rays taken to get a better view of blood flow in these veins.
- Is there a way to prevent this condition? Yes, and the answer lies in your lifestyle. Lifestyle does matter! Obesity can worsen or cause onset in people with genetic predisposition. So getting down to a healthy weight, calf-strengthening exercises and elevating legs can prevent onset as well as aggravation of symptoms.
- Let’s also talk about available treatment options. Minor varicose veins can be treated by laser and sclerotherapy. Endothermal ablation involves closing a vein by applying heat through a needle to numb the vein.
Some new procedures involve scelrosing agents (which are medications that numb veins by causing irritation) and adhesive agents that seal a vein shut.
- Treatments are available and effective but remember these aren’t a cure! Another set of varicose veins may pop out at another or the same place.
Thus, it is worth reiterating that a healthy active lifestyle goes a long way in keeping varicose veins from appearing as well as worsening further.
We hope this article has provided valuable insights into varicose veins. If you have tips or experiences on managing varicose veins, share them in the comments below. For further information or guidance, reach out to our certified experts by subscribing to GOQii’s Personalised Health Coaching here.
#BeTheForce
 When it comes to nutrition and fitness, Flaxseeds (Lineseeds/Alsi) is the most commonly heard terms these days. The way fashion trends keep pouring in, you will see food ingredients also hitting the market as and when research finds out something important.
When it comes to nutrition and fitness, Flaxseeds (Lineseeds/Alsi) is the most commonly heard terms these days. The way fashion trends keep pouring in, you will see food ingredients also hitting the market as and when research finds out something important.
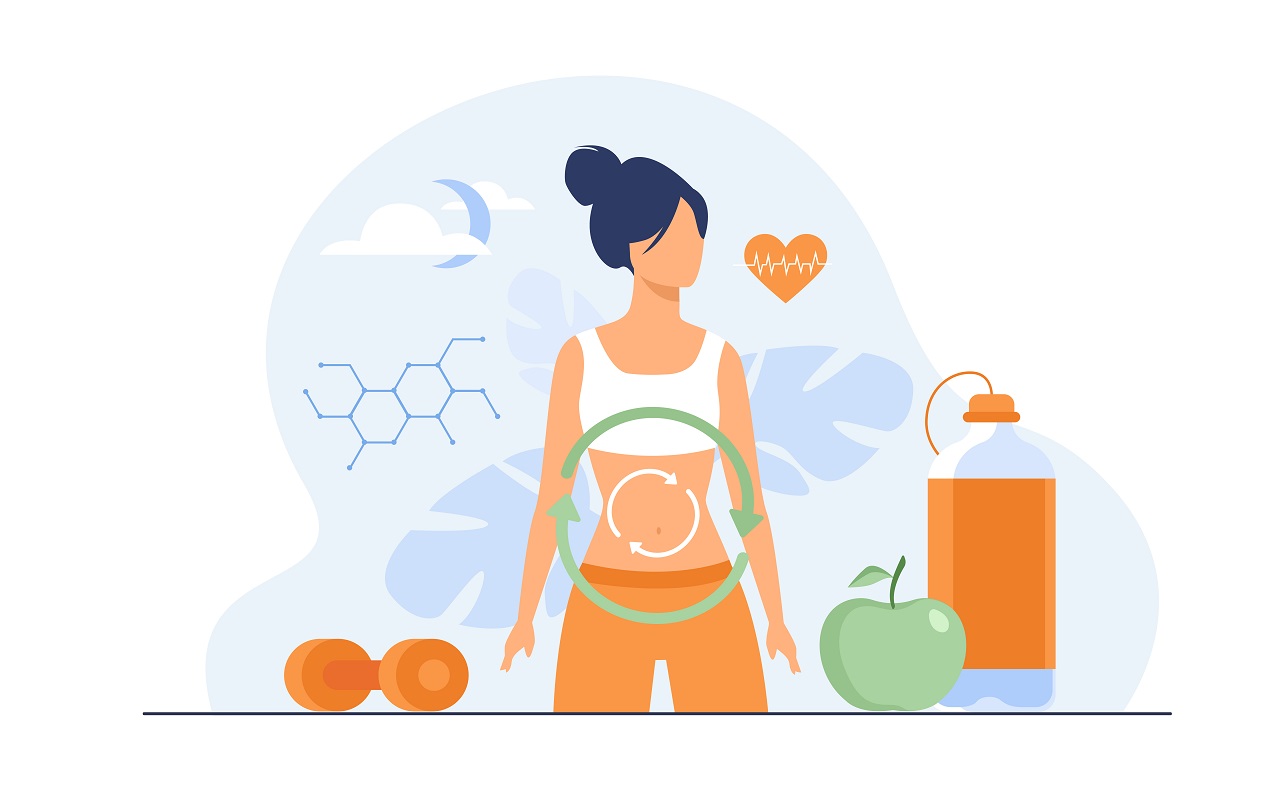
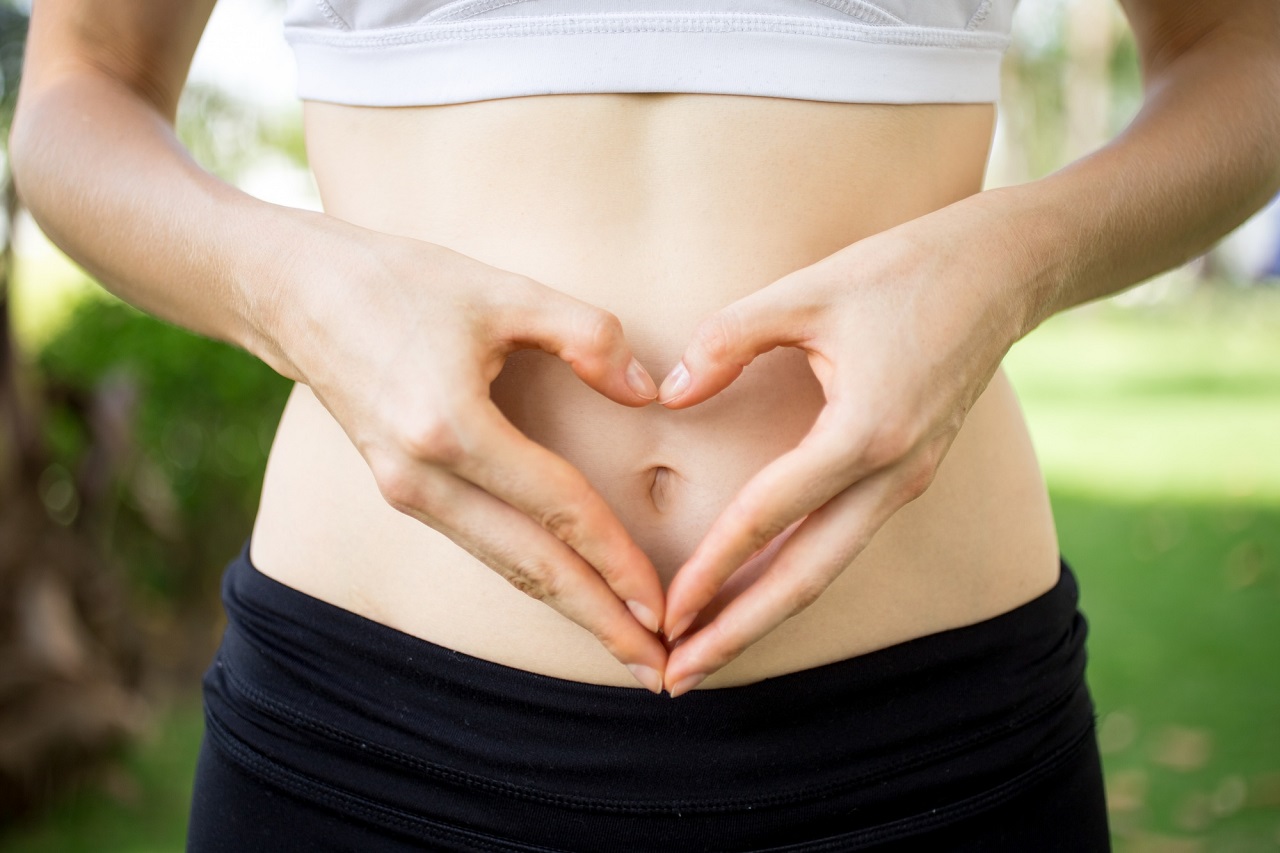 Gut health is a familiar concept, and it’s widely recognized that maintaining a healthy gut is beneficial for our overall well-being. Beyond just aiding digestion, a healthy gut supports our immune system, heart health, brain function, weight management, and numerous other facets of health.
Gut health is a familiar concept, and it’s widely recognized that maintaining a healthy gut is beneficial for our overall well-being. Beyond just aiding digestion, a healthy gut supports our immune system, heart health, brain function, weight management, and numerous other facets of health.



