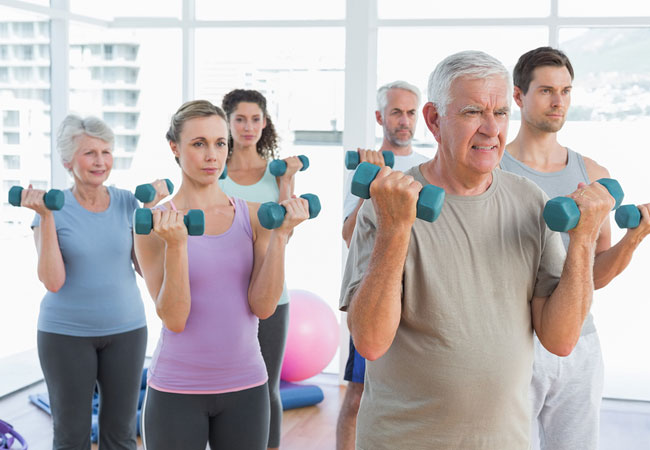
As you grow older it become imperative to work towrads building strength. The elderly need strength training more and more as they grow older to stay mobile for their everyday activities. The less active a person’s lifestyle, the earlier age-related changes will manifest.
According to International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF), Nutrition working Group examines role of Nutrition in Sarcopenia, with focus on protein, vitamin D and B, and acid-based diet.
Age-related muscle loss, called sarcopenia, is a natural part of aging. An article published in Harvard Health said that after age 30, you begin to lose as much as 3% to 5% per decade. Sarcopenia is a common consequence of aging, and poses a significant risk factor for disability in older adults. As muscle strength plays an important role in the tendency to fall, sarcopenia leads to an increased risk of fractures and other injuries.
Quoting from an article in Harvard Health, according to Dr. Thomas W. Storer, director of the exercise physiology and physical function lab at Harvard-affiliated Brigham and Women’s Hospital, just because you lose muscle does not mean its gone forever. The elderly can increase muscle mass lost as a consequence of aging. “
The International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) Nutrition Working Group has published a new review which identifies nutritional factors that contributes to loss of muscle mass, or conversely, are beneficial to the maintenance of muscle mass. The Group reviewed evidence on worldwide studies on the role of nutrition in sarcopenia, specifically looking at protein, acid-base balance, vitamin D/calcium, and other minor nutrients like B vitamins.
The most obvious intervention against sarcopenia is exercise in the form of resistance training. However, adequate nutritional intake and an optimal dietary acid-base balance are also very important elements of any strategy to preserve muscle mass and strength during aging.
The review discusses and identifies the following important nutritional factors that have been shown to be beneficial to the maintenance of muscle mass and the treatment and prevention of sarcopenia:
- Protein: Your diet also plays a role in building muscle mass. Protein is the king of muscle food. The body breaks it down into amino acids, which it uses to build muscle. The authors of the study propose an intake of 1.0-1.2 g/kg of body weight per day as optimal for skeletal muscle and bone health in elderly people without severely impaired renal function. .”While food sources are the best, supplemental protein can help if you struggle with consuming enough calories and protein from your regular diet,” says Dr. Storer.
- Vitamin D: As many studies indicate a role for vitamin D in the development and preservation of muscle mass and function, adequate Vitamin D should be ensured through exposure to sunlight and/or supplementation if required. Vitamin D supplementation in seniors, and specially in institutionalized elderly, is recommended for optimal musculoskeletal health.
- Avoiding dietary acid loads: Excess intake of acid-producing nutrients (meat and cereal grains) in combination with low intake of alkalizing fruits and vegetable may have negative effects on musculoskeletal health. Modifying the diet to include more fruits and vegetables is likely to benefit both bones and muscles. Emerging evidence also suggests that vitamin B12 and/or folic acid play a role in improving muscles function and strength.
The Review discusses non-nutritional interventions such as hormones, and calls for more studies to identify the potential of antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds in the prevention of Sarcopenia.
Strategies to reduce the numbers of falls and fractures within aging populations must include measures to prevent sarcopenia. At present, the available evidence suggests that combining resistance training with optimal nutritional status has a synergistic effect in preventing and treating sarcopenia.
Check with your doctor before embarking on any kind of strength-training routine. Then have a well-qualified personal trainer to help set up a detailed routine and supervise your initial workouts to ensure you perform them safely and in the best manner.