 Mr Rebello, sitting in front of me recalled his plight of waking up 2-3 times every night to void urine instead of only once as before. Initially, he assumed it was due to winter but, when the problem persisted in summer as well, he blamed it on his poorly controlled diabetes. He was 65 yrs of age when he began to experience this. He didn’t bother visiting his physician since he had made peace with his high blood sugars as he had no control over his eating habits.
Mr Rebello, sitting in front of me recalled his plight of waking up 2-3 times every night to void urine instead of only once as before. Initially, he assumed it was due to winter but, when the problem persisted in summer as well, he blamed it on his poorly controlled diabetes. He was 65 yrs of age when he began to experience this. He didn’t bother visiting his physician since he had made peace with his high blood sugars as he had no control over his eating habits.
How he wished he hadn’t assumed and instead consulted his physician. After 2 yrs he moved to another city and didn’t feel up to the task of finding a new physician to follow up with. Five years down the line, after his 70th birthday, he began experiencing lower back pain which he again concluded was due to ageing. Only when the pain became persistent and unbearable, he met an Orthopedic who after examination and X-rays diagnosed him with a collapsed vertebral fracture. He was crestfallen when the cause of his vertebral fracture was pinned down to ‘PROSTATE CANCER’.
Going back to the time when Mr Rebello was 65 yrs old, he overlooked the fact that the frequency of urination was normal during the day. Had high sugar been the cause, the issue would have bothered him during the day as well. Actually, this was the first symptom that his prostate gland was enlarged. Undiagnosed and untreated over 5 yrs the non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate had turned cancerous and spread to his backbone.
Let’s try to make sense about what the prostate gland is, its enlargement and when does it translate into cancer.
The Prostate Gland: Location in the body and function.
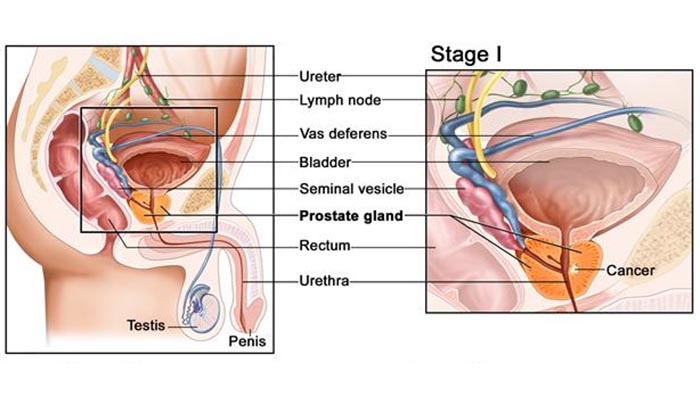
The image below shows the location of the prostate gland in the body which is present only in males. It is located below the urinary bladder. The prostate secretes the fluid that nourishes and protects sperms. During ejaculation, the prostate squeezes this fluid into the urethra, and it’s expelled with sperms as semen. In the prostatic cells, the male sex hormone testosterone gets converted to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) which causes the cells to grow resulting in an increase in its size.
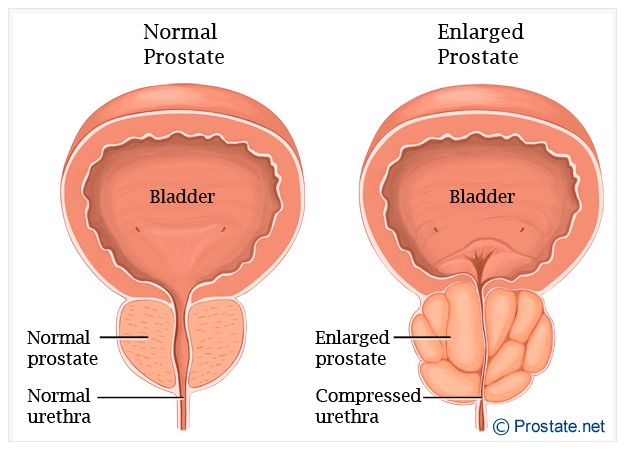
Normally, the prostate gland is approximately the size of a walnut. As the size increases with age (which can start as early as 40 yrs) it starts to obstruct the urine outflow as shown in the image.
Symptoms of Prostatic enlargement:
- A weak or slow urinary stream.
- A feeling of incomplete bladder emptying.
- Difficulty starting urination.
- Frequent urination.
- The urgency to urinate.
- Getting up frequently at night to urinate.
- A urinary stream that starts and stops.
- Straining to urinate.
Medically enlarged prostate which is not cancerous is called Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH).
As the gland keeps getting enlarged, there are mutations in the DNA of its cells causing it to grow uncontrolled and abnormally resulting in cancer.
The saving grace in this entire process is that prostatic enlargement can be diagnosed early and controlled thereby preventing cancer.
DIAGNOSTIC MODALITIES:
- Sonography of the prostate gland is advised once a man turns 50 yrs to establish if enlargement has started. If there is a family history of prostate cancer then it should be done as early as 40 yrs.
- A blood test called Prostate Specific Antigen(PSA) should be done. Very high values are suggestive of cancer whereas in the enlargement phase the values remain < 4 units.
If you are facing any of the above symptoms, you must visit a Urologist who will diagnose and prescribe medication for the same. Incase medicines are not effective, one might have to opt for surgery.
In Mr Rebello’s case, since cancer had already developed, radiotherapy was first given to shrink the size of the prostate, post which surgery was performed to remove the cancerous gland. Cancer which had spread to his backbone was controlled by a combination of chemo and hormonal therapy.
Risk Factors for prostatic enlargement and cancer:
Age – prevalence increases markedly with age. The gland grows at a rate of 2 – 2.5 % annually in older men.
Genetics – 50% men undergoing surgery for BPH < 60 yrs of age have inheritable form of the disease.
PREVENTION:
Apart from timely diagnosis and treatment, being physically active, controlling Diabetes and weight are known to reduce enlargement of the gland. Diet rich in antioxidants and vitamins is also beneficial in prevention along with avoiding red meat.
Image credit – prostate.net





