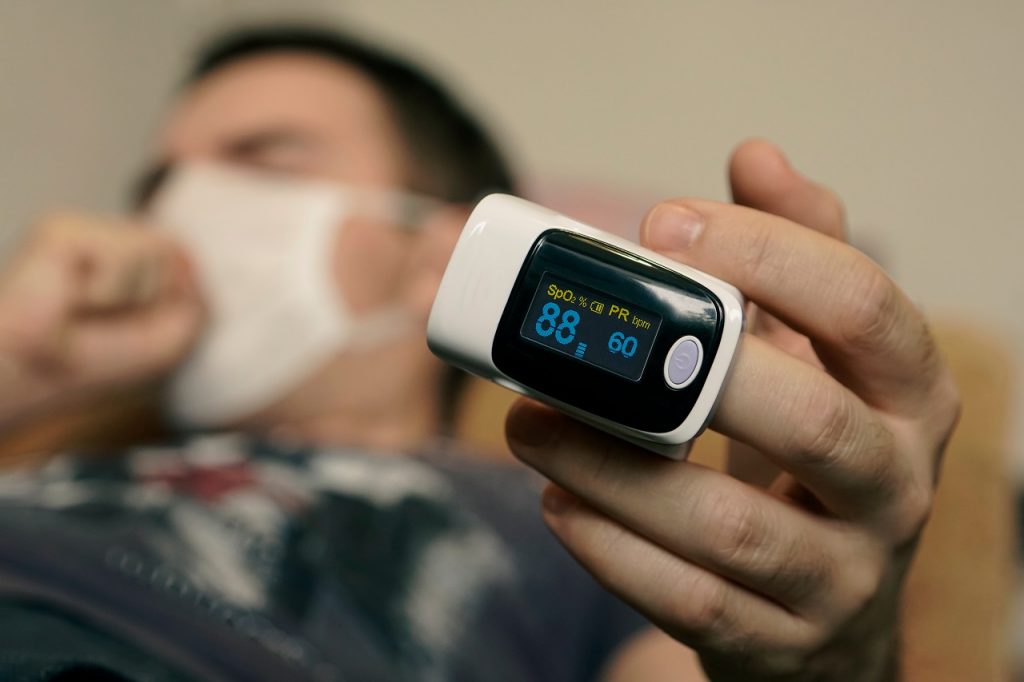
 Blood Oxygen levels, also known as oxygen saturation or SpO2, is the amount of oxygenated haemoglobin circulating in the blood i.e it indicates how well the body carries oxygen to all parts of the body. Most of the oxygen in the body is carried by the red blood cells, which collect oxygen from the lungs and deliver it to different parts of the body. Oxygen levels above 95-100 are considered normal and a value between 91-94 requires regular monitoring (prone breathing helps improve levels in this situation), values below 91 indicates hypoxemia, low blood oxygen levels.
Blood Oxygen levels, also known as oxygen saturation or SpO2, is the amount of oxygenated haemoglobin circulating in the blood i.e it indicates how well the body carries oxygen to all parts of the body. Most of the oxygen in the body is carried by the red blood cells, which collect oxygen from the lungs and deliver it to different parts of the body. Oxygen levels above 95-100 are considered normal and a value between 91-94 requires regular monitoring (prone breathing helps improve levels in this situation), values below 91 indicates hypoxemia, low blood oxygen levels.
The second wave of COVID-19 is affecting the youth more than the elderly. Reports suggest that the younger generation is taking time to realize the infection in their bodies which is spreading the virus more rapidly. In spite of low blood oxygen levels, a person shows no signs – a condition known as happy hypoxia (low levels of oxygen at tissue levels).
The most efficient way to measure blood oxygen level is through an ABG test, which requires a blood sample of a person and is done in a laboratory. So, an alternative test can be done using a small device known as a pulse oximeter – a small device which is clipped on a person’s finger. It measures the blood oxygen by light absorption through a person’s pulse. This is not very accurate compared to the ABG test as it depends on many factors like dirty fingers, nail polish and poor circulation to the extremities.
Symptoms of Low Oxygen Levels
- Shortness of breath or breathlessness is an uncomfortable condition which makes it difficult to get air fully into the lungs
- Throbbing headache: lack of oxygen in the brain causes sudden and rapid increase in blood pressure in the brain, leading to throbbing headache
- Restlessness is a feeling to constantly move, not being able to calm the mind or a combination of both.
- Dizziness and confusion is a feeling of lightheadedness or a feeling of fainting while confusion is a situation when a person is not able to think straight. Dizziness is a temporary feeling which might come and go while confusion affects a person’s thinking capacity. Extremely low levels of oxygen can also lead to loss of consciousness or inability to stay awake or even get up.
- Rapid breathing: Low oxygen levels in the blood causes shortness of breath and a hunger for air. Because of incomplete exhalation, carbon-di-oxide concentration increases in the body causing rapid breathing
- Chest pain: Not getting enough oxygen into the lungs creates an urge to breathe deep and this repeated action causes pain and discomfort in the chest.
- High blood pressure: Low levels of oxygen in the blood narrows down the pulmonary arteries which squeezes the blood into a narrow space, leading to increased blood pressure.
- Changes in colour of skin, lips or the extremities to blue or cherry red or shades varying between the two known as cyanosis usually happens when oxygen levels are extremely low and the person feels too cold to touch.
- Lack of coordination also called coordination impairment happens when there is disruption in communication between the brain and the rest of the body. Walking does not require much effort on a regular basis but when a person has low oxygen levels, they might wobble or have difficulty in lifting their legs. This usually happens when there is less oxygen supply to the brain.
- Visual disorders: Lack of oxygen supply to the eyes causes blurred vision, burning, excessive tearing and scratching. Excessive tear production is due to inflammation of the glands in the eyes or blockage of tear ducts. There could also be redness of the eyes due to inflammation of the conjunctiva.
- Sense of euphoria is a feeling of excitement and happiness. Some people show symptoms of a high, which you usually have when taking drugs or side effects of any medicine. This is due to the lack of oxygen which creates confusion and people fail to realize their oxygen levels are low.
- Rapid heartbeat: The heart sends electrical signals which make it beat and pump blood. This signal begins in the upper right chamber of the heart called the Sino Atrial Node, also the pacemaker which controls heartbeat. These electrical signals are controlled by the Autonomic Nervous System and low oxygen levels make the ANS transmit these signals at a faster rate and increase the demand for more oxygen causing rapid heart rate
The above-mentioned symptoms and the complications can easily be prevented when a person is alert and knows the symptom and measures their blood oxygen levels or SpO2 on a regular basis. SpO2, along with other symptoms of COVID-19 such as high body temperature can be easily monitored through the GOQii Smart Vital. As the new wave of COVID is said to affect children, you might also consider getting the GOQii Smart Vital Junior for your kids and imbibe healthy habits in them from a young age!
We hope this article helps. For more on COVID-19, check out Healthy Reads or tune in to LIVE sessions by experts on GOQii Play. To get these tips and support directly from your GOQii Coach, subscribe to personalized coaching now: https://goqiiapp.page.link/wssu
Stay home, stay safe and #BeTheForce



